Correlation Coefficient
The correlation coefficient is a statistical measure of the strength of the relationship between the relative movements of two variables. \\textbf{where:} \\\\ &\\rho\_{xy} = \\text{Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient} \\\\ &\\text{Cov} ( x, y ) = \\text{covariance of variables } x \\text{ and } y \\\\ &\\sigma\_x = \\text{standard deviation of } x \\\\ &\\sigma\_y = \\text{standard deviation of } y \\\\ \\end{aligned} ρxy\=σxσyCov(x,y)where:ρxy\=Pearson product-moment correlation coefficientCov(x,y)\=covariance of variables x and yσx\=standard deviation of xσy\=standard deviation of y Standard deviation is a measure of the dispersion of data from its average. correlation coefficient Cov ( x , y ) \= covariance of variables x and y σ x \= standard deviation of x σ y \= standard deviation of y \\begin{aligned} &\\rho\_{xy} = \\frac { \\text{Cov} ( x, y ) }{ \\sigma\_x \\sigma\_y } \\\\ & A correlation of -1.0 shows a perfect negative correlation, while a correlation of 1.0 shows a perfect positive correlation. For example, a correlation coefficient could be calculated to determine the level of correlation between the price of crude oil and the stock price of an oil-producing company, such as Exxon Mobil Corporation.

What Is the Correlation Coefficient?
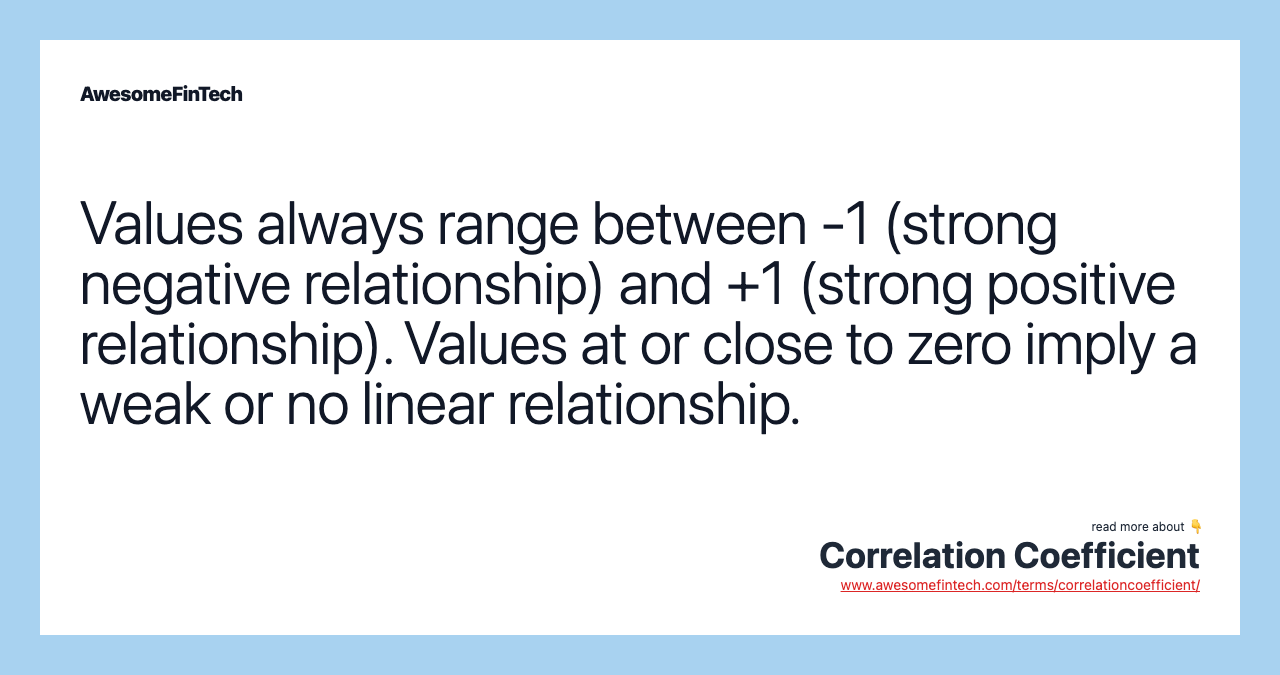
The correlation coefficient is a statistical measure of the strength of the relationship between the relative movements of two variables. The values range between -1.0 and 1.0. A calculated number greater than 1.0 or less than -1.0 means that there was an error in the correlation measurement. A correlation of -1.0 shows a perfect negative correlation, while a correlation of 1.0 shows a perfect positive correlation. A correlation of 0.0 shows no linear relationship between the movement of the two variables.
Correlation statistics can be used in finance and investing. For example, a correlation coefficient could be calculated to determine the level of correlation between the price of crude oil and the stock price of an oil-producing company, such as Exxon Mobil Corporation. Since oil companies earn greater profits as oil prices rise, the correlation between the two variables is highly positive.


Understanding the Correlation Coefficient
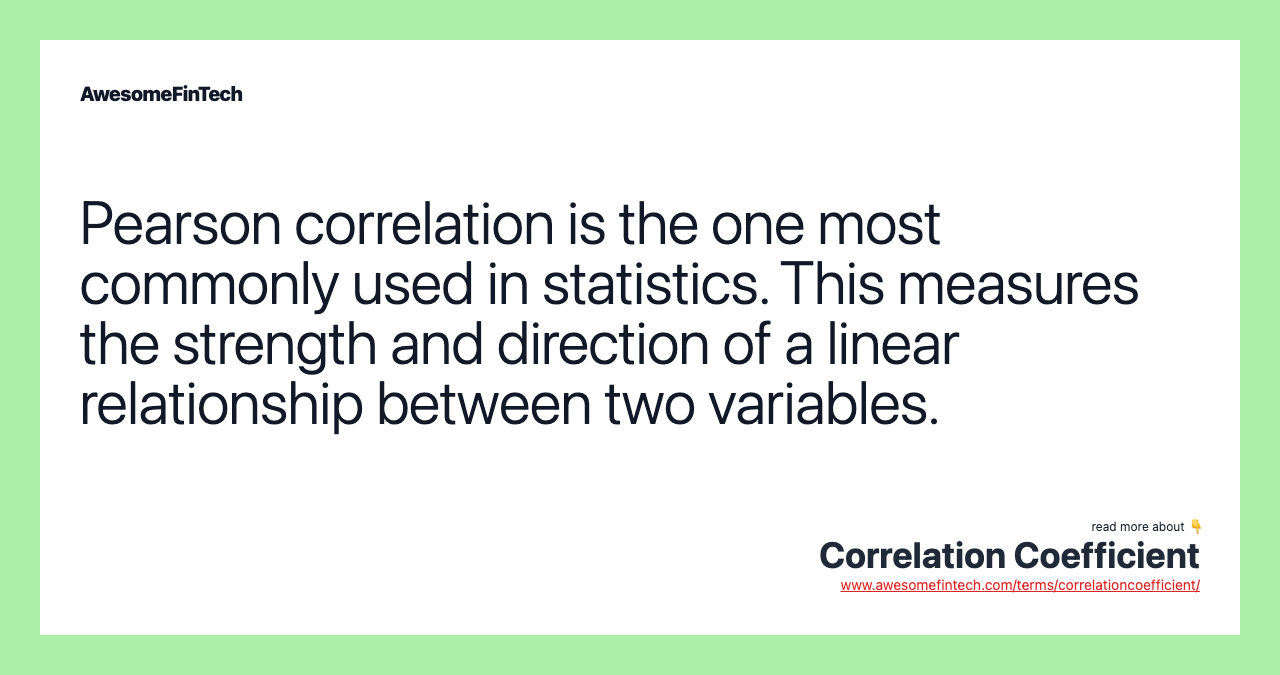
There are several types of correlation coefficients, but the one that is most common is the Pearson correlation (r). This measures the strength and direction of the linear relationship between two variables. It cannot capture nonlinear relationships between two variables and cannot differentiate between dependent and independent variables.
A value of exactly 1.0 means there is a perfect positive relationship between the two variables. For a positive increase in one variable, there is also a positive increase in the second variable. A value of -1.0 means there is a perfect negative relationship between the two variables. This shows that the variables move in opposite directions — for a positive increase in one variable, there is a decrease in the second variable. If the correlation between two variables is 0, there is no linear relationship between them.
The strength of the relationship varies in degree based on the value of the correlation coefficient. For example, a value of 0.2 shows there is a positive correlation between two variables, but it is weak and likely unimportant. Analysts in some fields of study do not consider correlations important until the value surpasses at least 0.8. However, a correlation coefficient with an absolute value of 0.9 or greater would represent a very strong relationship.
Investors can use changes in correlation statistics to identify new trends in the financial markets, the economy, and stock prices.
Correlation Statistics and Investing
The correlation between two variables is particularly helpful when investing in the financial markets. For example, a correlation can be helpful in determining how well a mutual fund performs relative to its benchmark index, or another fund or asset class. By adding a low or negatively correlated mutual fund to an existing portfolio, the investor gains diversification benefits.
In other words, investors can use negatively correlated assets or securities to hedge their portfolios and reduce market risk due to volatility or wild price fluctuations. Many investors hedge the price risk of a portfolio, which effectively reduces any capital gains or losses because they want the dividend income or yield from the stock or security.
Correlation statistics also allow investors to determine when the correlation between two variables changes. For example, bank stocks typically have a highly positive correlation to interest rates, since loan rates are often calculated based on market interest rates. If the stock price of a certain bank is falling while interest rates are rising, investors can glean that something's askew with that particular bank. If the stock prices of other banks in the sector are also rising, investors can conclude that the decline of the outlier bank's stock is not due to interest rates. Instead, the poorly performing bank is likely dealing with an internal, fundamental issue.
Correlation Coefficient Equation
To calculate the Pearson product-moment correlation, one must first determine the covariance of the two variables in question. Next, one must calculate each variable's standard deviation. The correlation coefficient is determined by dividing the covariance by the product of the two variables' standard deviations.
ρ x y = Cov ( x , y ) σ x σ y where: ρ x y = Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient Cov ( x , y ) = covariance of variables x and y σ x = standard deviation of x σ y = standard deviation of y \begin{aligned} &\rho_{xy} = \frac { \text{Cov} ( x, y ) }{ \sigma_x \sigma_y } \\ &\textbf{where:} \\ &\rho_{xy} = \text{Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient} \\ &\text{Cov} ( x, y ) = \text{covariance of variables } x \text{ and } y \\ &\sigma_x = \text{standard deviation of } x \\ &\sigma_y = \text{standard deviation of } y \\ \end{aligned} ρxy=σxσyCov(x,y)where:ρxy=Pearson product-moment correlation coefficientCov(x,y)=covariance of variables x and yσx=standard deviation of xσy=standard deviation of y
Standard deviation is a measure of the dispersion of data from its average. Covariance is a measure of how two variables change together, but its magnitude is unbounded, so it is difficult to interpret. By dividing covariance by the product of the two standard deviations, one can calculate the normalized version of the statistic. This is the correlation coefficient.
What Is Meant by the Correlation Coefficient?
The correlation coefficient describes how one variable moves in relation to another. A positive correlation indicates that the two move in the same direction, with a +1.0 correlation when they move in tandem. A negative correlation coefficient tells you that they instead move in opposite directions. A correlation of zero suggests no correlation at all.
How Do You Calculate the Correlation Coefficient?
The correlation coefficient is calculated by first determining the covariance of the variables and then dividing that quantity by the product of those variables’ standard deviations.
How Is the Correlation Coefficient Used in Investing?
Correlation coefficients are a widely-used statistical measure in investing. They play a very important role in areas such as portfolio composition, quantitative trading, and performance evaluation. For example, some portfolio managers will monitor the correlation coefficients of individual assets in their portfolios in order to ensure that the total volatility of their portfolios is maintained within acceptable limits.
Similarly, analysts will sometimes use correlation coefficients to predict how a particular asset will be impacted by a change to an external factor, such as the price of a commodity or an interest rate.
Related terms:
Business Valuation , Methods, & Examples
Business valuation is the process of estimating the value of a business or company. read more
Coefficient of Determination: Overview
The coefficient of determination is a measure used in statistical analysis to assess how well a model explains and predicts future outcomes. read more
Correlation
Correlation is a statistical measure of how two securities move in relation to each other. read more
Dispersion
Dispersion is a statistical measure of the expected volatility of a security based on historical returns. read more
Diversification
Diversification is an investment strategy based on the premise that a portfolio with different asset types will perform better than one with few. read more
Inverse Correlation
An inverse correlation is a relationship between two variables such that when one variable is high the other is low and vice versa. read more
Linear Relationship
A linear relationship (or linear association) is a statistical term used to describe the directly proportional relationship between a variable and a constant. read more
Negative Correlation
Negative correlation is a relationship between two variables in which one variable increases as the other decreases, and vice versa. read more
Pearson Coefficient
Pearson coefficient is a type of correlation coefficient that represents the relationship between two variables that are measured on the same interval. read more
Positive Correlation
Positive correlation is a relationship between two variables in which both variables move in tandem. read more