Mortality and Expense Risk Charge
A mortality and expense risk charge is a fee imposed on investors in annuities and other products offered by insurance companies. Generally, an underwriter will consider three factors in determining mortality and expense risk charges: the net amount at risk under the policy, the risk classification of the policyholder, and the age of the policyholder. The insurance company will invest the largest chunk of a premium into a savings fund, and it will be returned to the policyholder at the time of maturity and to the nominee when the policyholder dies. The mortality and expense risk charge protects the insurance company against unexpected events, including the untimely death of the policyholder. That's why a mortality and expense risk charge is calculated whenever an insurance company offers an annuity to a client. With variable annuities, the mortality and expense risk charge is applied only to funds held in individual accounts, not funds held in the general account.

What Is a Mortality and Expense Risk Charge?
A mortality and expense risk charge is a fee imposed on investors in annuities and other products offered by insurance companies. It compensates the insurer for any losses that it might suffer as a result of unexpected events, including the death of the annuity holder.
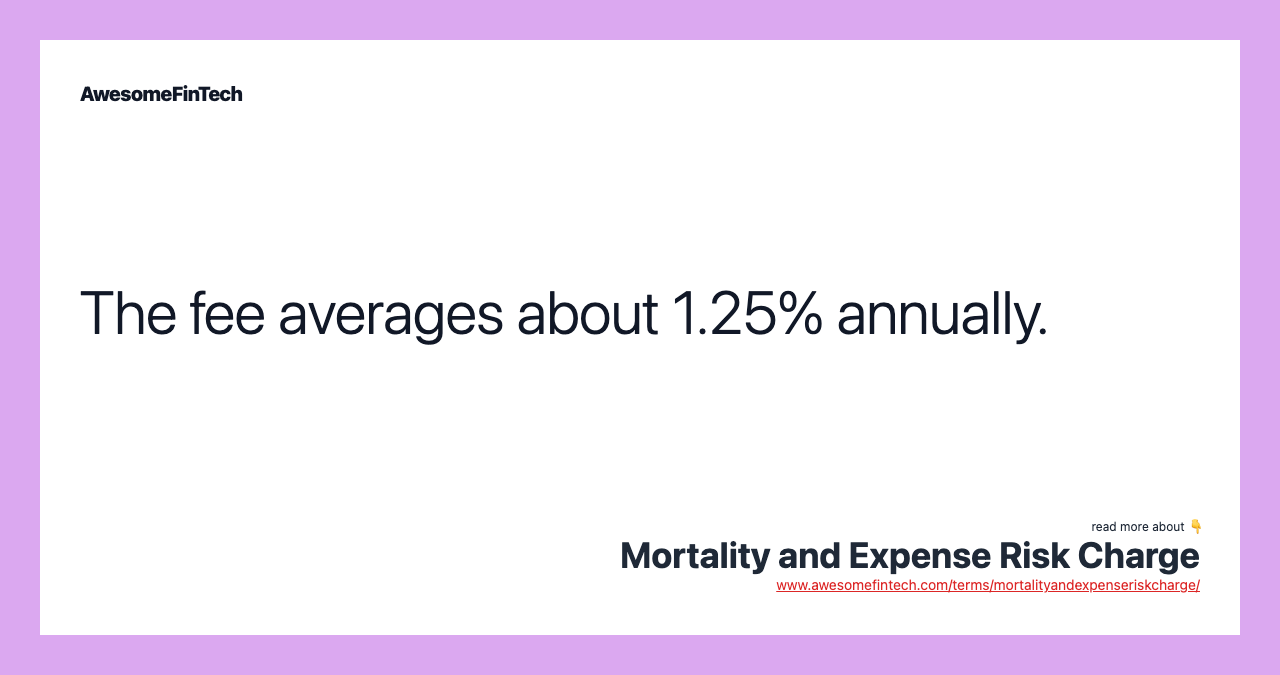
The amount of the fee varies according to a number of factors including the age of the investor. The average fee is about 1.25% per year. The mortality risk is the chance that the company will have to pay out a death benefit sooner than expected.


Understanding the Mortality and Expense Risk Charge
A lifetime annuity provides the investor with a degree of certainty about his or her income after retirement, but there's some uncertainty there for the insurance company.
That's why a mortality and expense risk charge is calculated whenever an insurance company offers an annuity to a client. The charge is based on assumptions about the life expectancy of the client and the likelihood of various other adverse events.
The mortality and expense charge is intended to offset the cost to the insurer of any income guarantees that might be included with the annuity contract.
The mortality risk specifically addresses the risk that the contract holder will die at a time when the account balance is less than the premiums that have been paid on the policy and any withdrawals that have already been made.
The younger the applicant is, the lower the mortality and expense risk will be.
The total mortality and expense risk charge ranges from about 0.40% to about 1.75 per year. Most insurers annualize this expense and deduct it once a year.
With variable annuities, the mortality and expense risk charge is applied only to funds held in individual accounts, not funds held in the general account.
Calculating Mortality and Expense Risk Charges
Generally, an underwriter will consider three factors in determining mortality and expense risk charges: the net amount at risk under the policy, the risk classification of the policyholder, and the age of the policyholder.
The insurance company will invest the largest chunk of a premium into a savings fund, and it will be returned to the policyholder at the time of maturity and to the nominee when the policyholder dies.
If you purchase life insurance at a young age, you'll benefit from reduced mortality charges. This is based on the simple logic that an older person is more likely to die than a younger one. A 25-year-old will have a higher life expectancy than a 55-year-old and will benefit from a lower mortality charge.
Related terms:
Annuities: Insurance for Retirement
An annuity is a financial product that pays out a fixed stream of payments to an individual, primarily used as an income stream for retirees. read more
Classified Insurance
Classified Insurance is coverage provided to a policyholder that is considered more risky and thus less desirable to the insurer. read more
L Share Annuity Class
The L share annuity class is a version of a variable annuity that starts paying out earlier than most but has relatively high administrative costs. read more
Life Expectancy
Life expectancy is defined as the age to which a person is expected to live, or the remaining number of years a person is expected to live. read more
Life Insurance Guide to Policies and Companies
Life insurance is a contract in which an insurer, in exchange for a premium, guarantees payment to an insured’s beneficiaries when the insured dies. read more
Voluntary Accidental Death And Dismemberment Insurance (VAD&D)
Voluntary accidental death and dismemberment insurance (VAD&D) pays cash in the event the policyholder is killed or loses a specific body part. read more