Impulse Wave Pattern
An impulse wave pattern is a technical trading term that describes a strong move in a financial asset's price coinciding with the main direction of the underlying trend. Impulse waves consist of five smaller-degree waves net moving in the same direction as a larger trend, while corrective waves are composed of three smaller-degree waves moving in the opposite direction. These impulse waves are shown in the illustration below as wave 1, wave 3 and wave 5, while collectively waves 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 form a five-wave impulse at one-larger degree. The number of waves in a five-wave impulse, the number of waves in a three-wave correction, and the number of waves in combinations thereof accord with Fibonacci numbers, a numeric sequence associated with growth and decay in life forms. Like all motive waves, it consists of five sub-waves; three of them are also motive waves, and two are corrective waves.

What Is an Impulse Wave Pattern?
An impulse wave pattern is a technical trading term that describes a strong move in a financial asset's price coinciding with the main direction of the underlying trend. It is used frequently in discussion of the Elliott Wave theory, a method for analyzing and predicting financial market price movements. Impulse waves can refer to upward movements in uptrends or downward movements in downtrends.


Understanding Impulse Waves
The interesting thing about impulse wave patterns in relation to the Elliott Wave theory is that they are not limited to a certain time period. This allows some waves to last for several hours, several years or even decades. Regardless of the time frame used, impulse waves always run in the same direction as the trend at one-larger degree. These impulse waves are shown in the illustration below as wave 1, wave 3 and wave 5, while collectively waves 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 form a five-wave impulse at one-larger degree.
Image by Julie Bang © Investopedia 2020
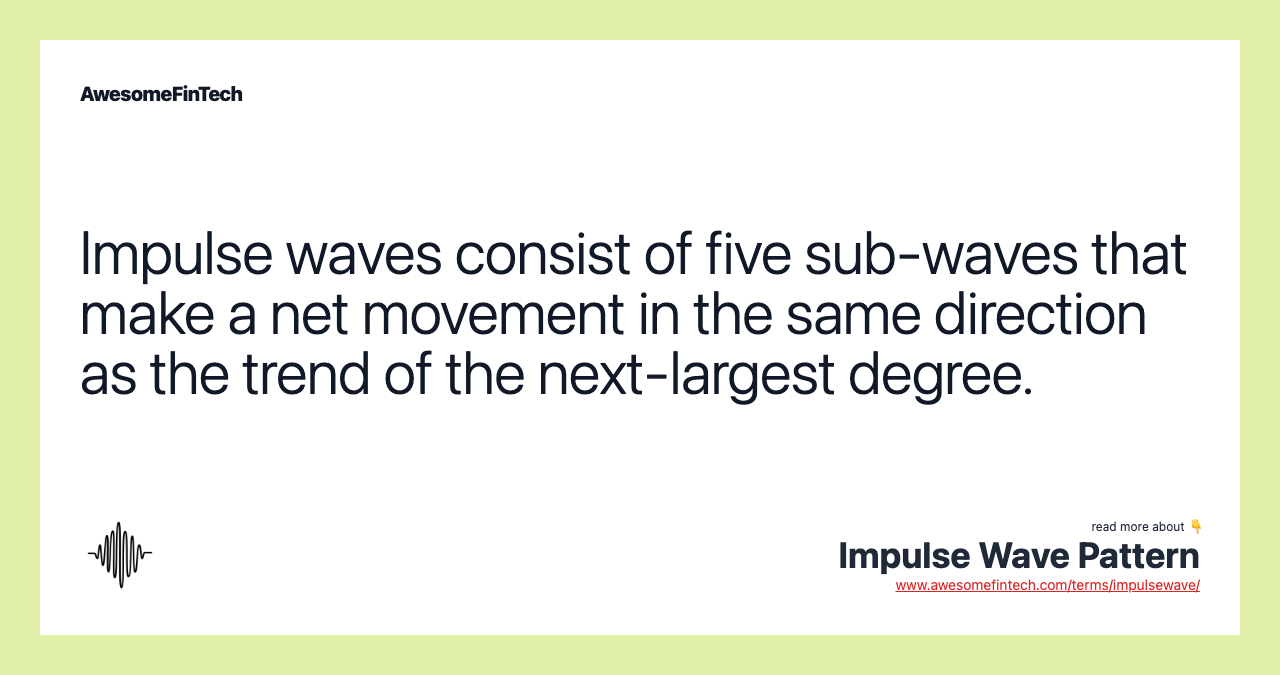
Impulse waves consist of five sub-waves that make net movement in the same direction as the trend of the next-largest degree. This pattern is the most common motive wave and the easiest to spot in a market. Like all motive waves, it consists of five sub-waves; three of them are also motive waves, and two are corrective waves. This is labeled as a 5-3-5-3-5 structure, which was shown above. However, it has three rules that define its formation. These rules are unbreakable. If one of these rules is violated, then the structure is not an impulse wave and one would need to re-label the suspected impulse wave. The three rules are: wave two cannot retrace more than 100 percent of wave one; wave three can never be the shortest of waves one, three and five.
Elliott Wave Theory
Elliott Wave theory was formulated by R.N. Elliott in the 1930s based on his study of 75 years of stock charts covering various time periods. Elliott, whose theory gained adoption in the investment community, designed it to provide insights into the probable future direction of larger price movements in the equity market. The theory can be used in conjunction with other technical analysis to pinpoint potential opportunities.
The theory seeks to ascertain market price direction through the study of impulse wave and corrective wave patterns. Impulse waves consist of five smaller-degree waves net moving in the same direction as a larger trend, while corrective waves are composed of three smaller-degree waves moving in the opposite direction. To the theory's advocates, a bull market consists of a five-wave impulse and a bear market consists of a corrective retracement, regardless of size.
The number of waves in a five-wave impulse, the number of waves in a three-wave correction, and the number of waves in combinations thereof accord with Fibonacci numbers, a numeric sequence associated with growth and decay in life forms. Elliott noticed that wave retracements often conform to Fibonacci ratios, such as 38.2% and 61.8%, which are based on the golden ratio of 1.618. Wave patterns are also a part of the Elliott Wave oscillator, a tool inspired by Elliott Wave theory that depicts price patterns as positive or negative above or below a fixed horizontal axis.
Elliott Wave theory continues to be a popular trading tool thanks to the work of Robert Prechter and his colleagues at Elliott Wave International, a market research firm formed to apply and enhance Elliott’s original work by integrating it with such current technologies as artificial intelligence.
Related terms:
Corrective Waves
Corrective waves are a set of price movements normally associated with the Elliott Wave Theory of technical analysis. read more
Downtrend
A downtrend refers to the price action of a security that moves lower in price as it fluctuates over time. read more
Elliott Wave Theory
The Elliott Wave theory is a technical analysis toolkit used to predict price movements by observing and identifying repeating patterns of waves. read more
Fibonacci Extensions
Fibonacci extensions are a method of technical analysis commonly used to aid in placing profit targets. read more
Fibonacci Numbers Lines and Uses
Fibonacci numbers and lines are technical tools for traders based on a mathematical sequence developed by an Italian mathematician. These numbers help establish where support, resistance, and price reversals may occur. read more
Fibonacci Retracement Levels
Fibonacci retracement levels are horizontal lines that indicate where support and resistance are likely to occur. They are based on Fibonacci numbers. read more
Technical Analysis of Stocks and Trends
Technical analysis of stocks and trends is the study of historical market data, including price and volume, to predict future market behavior. read more
Technical Analysis
Technical analysis is a trading discipline that seeks to identify trading opportunities by analyzing statistical data gathered from trading activity. read more
Uptrend
Uptrend is a term used to describe an overall upward trajectory in price. Many traders opt to trade during uptrends with specific trending strategies. read more
Wolfe Wave
A Wolfe Wave is a pattern used in technical analysis to time trades around a breakout. read more