Hazard Rate
The hazard rate refers to the rate of death for an item of a given age (x). A person aged 60 would have a higher probability of dying at age 65 than a person aged 30 because the person aged 30 still has many more units of time (years) left in his or her life, and the probability that the person will die during one specific unit of time is lower. In many instances, the hazard rate can resemble the shape of a bathtub. It is part of a larger equation called the hazard function, which analyzes the likelihood that an item will survive to a certain point in time based on its survival to an earlier time (t). It is part of a larger equation called the hazard function, which analyzes the likelihood that an item will survive to a certain point in time based on its survival to an earlier time (t). As you get older, you have a greater chance of dying at a specific age, since the average failure rate is calculated as a fraction of the number of units that exist in a specific interval, divided by the number of total units at the beginning of the interval.

More in Economy
What Is the Hazard Rate?
The hazard rate refers to the rate of death for an item of a given age (x). It is part of a larger equation called the hazard function, which analyzes the likelihood that an item will survive to a certain point in time based on its survival to an earlier time (t). In other words, it is the likelihood that if something survives to one moment, it will also survive to the next.
The hazard rate only applies to items that cannot be repaired and is sometimes referred to as the failure rate. It is fundamental to the design of safe systems in applications and is often relied on in commerce, engineering, finance, insurance, and regulatory industries.


Understanding the Hazard Rate
The hazard rate measures the propensity of an item to fail or die depending on the age it has reached. It is part of a wider branch of statistics called survival analysis, a set of methods for predicting the amount of time until a certain event occurs, such as the death or failure of an engineering system or component.
The concept is applied to other branches of research under slightly different names, including reliability analysis (engineering), duration analysis (economics), and event history analysis (sociology).
The Hazard Rate Method
The hazard rate for any time can be determined using the following equation:
h ( t ) = f ( t ) / R ( t ) h(t) = f(t) / R(t) h(t)=f(t)/R(t)
F(t) is the probability density function (PDF), or the probability that the value (failure or death) will fall in a specified interval, for example, a specific year. R(t), on the other hand, is the survival function, or the probability that something will survive past a certain time (t).
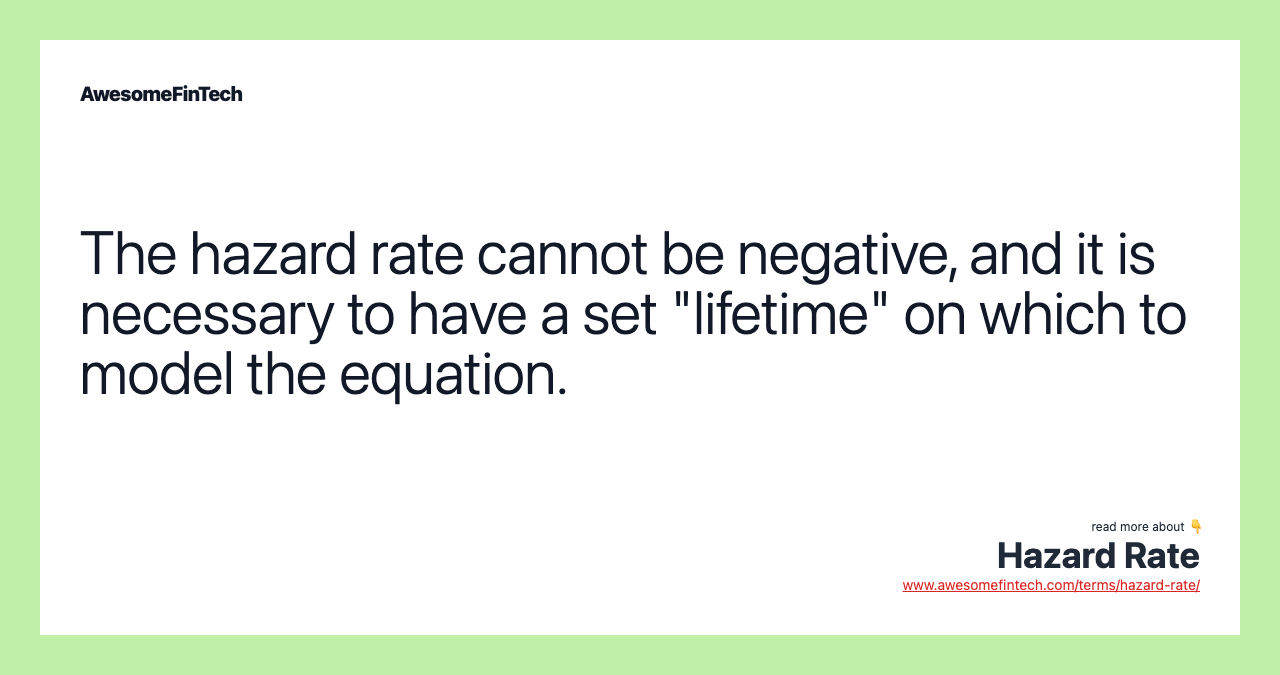
The hazard rate cannot be negative, and it is necessary to have a set "lifetime" on which to model the equation.
Example of the Hazard Rate
The probability density calculates the probability of failure at any given time. For instance, a person has a certainty of dying eventually. As you get older, you have a greater chance of dying at a specific age, since the average failure rate is calculated as a fraction of the number of units that exist in a specific interval, divided by the number of total units at the beginning of the interval.
If we were to calculate a person's chances of dying at a certain age, we would divide one year by the number of years that person potentially has left to live. This number would grow larger each year. A person aged 60 would have a higher probability of dying at age 65 than a person aged 30 because the person aged 30 still has many more units of time (years) left in his or her life, and the probability that the person will die during one specific unit of time is lower.
Special Considerations
In many instances, the hazard rate can resemble the shape of a bathtub. The curve slopes downwards at the beginning, indicating a decreasing hazard rate, then levels out to be constant, before moving upwards as the item in question ages.
Think of it this way: when an auto manufacturer puts together a car, its components are not expected to fail in its first few years of service. However, as the car ages, the probability of malfunction increases. By the time the curve slopes upwards, the useful life period of the product has expired and the chance of non-random issues suddenly occurring becomes much more likely.
Related terms:
Binomial Distribution
The binomial distribution is a probability distribution that summarizes the likelihood that a value will take one of two independent values. read more
Commerce
Commerce refers to the exchange of goods, services, or something of value between businesses or entities. read more
Duration
Duration indicates the years it takes to receive a bond's true cost, weighing in the present value of all future coupon and principal payments. read more
Economics : Overview, Types, & Indicators
Economics is a branch of social science focused on the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. read more
Inflation
Inflation is a decrease in the purchasing power of money, reflected in a general increase in the prices of goods and services in an economy. read more
Insurance
Insurance is a contract (policy) in which an insurer indemnifies another against losses from specific contingencies and/or perils. read more
Monte Carlo Simulation
Monte Carlo simulations are used to model the probability of different outcomes in a process that cannot easily be predicted. read more
Mortality Table
A mortality table shows the rate of deaths occurring in a defined population during a selected time interval or survival from birth to any given age. read more
Probability Density Function (PDF)
Probability density function is a statistical expression defining the likelihood of a series of outcomes for a discrete variable, such as a stock or ETF. read more
Poisson Distribution
A Poisson distribution is a statistical distribution showing the likely number of times that an event will occur within a specified period of time. read more